Bonus this content: Download this blogpost!
What does data retention mean?
Data retention, also called records retention, is the continued storage of an organisation’s data for compliance or business reasons. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) does not specify time limits for retention. However, the general principle is that data should only be kept for as long as it is needed. This is reflected in Article 5(1)(e) GDPR, also known as the storage limitation principle. This principle provides that even if personal data is collected fairly and lawfully, it cannot be kept longer than required to fulfil the purposes for which it was collected. Personal data may be kept for longer periods where it is archived in the public interest or for scientific or historical research, provided the data is appropriately anonymised or encrypted. Therefore, the onus is on the organisation to understand what data it holds, why it holds it, and where it no longer has an appropriate use for the data, whether it should be erased or anonymised.
Understanding Data Retention
Data retention refers to the practice of retaining data for a specific period of time, based on business, legal, or regulatory requirements. This can include data generated from various sources, such as email, social media, documents, and other electronic records.
Data retention policies determine how long data must be kept, what data must be kept, where it should be stored, and how it should be disposed of once it is no longer needed. These policies are typically based on factors such as organizational needs, industry standards, and legal requirements.
Can an organisation keep data just in case?
Some organisations decide to retain data it no longer needs just in case it might be needed in the future. This is not a sufficient justification to retain data under GDPR. Adopting an approach of retaining data just in case leads to a risk that data will become irrelevant, excessive, inaccurate, or out of date. In turn, this increases the danger that such data will be used erroneously to the detriment of the data subject’s rights and the organisation’s reputation. Organisations also need to consider the costs associated with retaining unnecessary data, including storage and security expenses. Further, retaining unnecessary data may make an organisation’s daily operations more difficult. For example, organisations that frequently receive subject access requests will have a difficult task satisfying that request within the time limits where they must sift through large quantities of unnecessary data.
Definition of Data Retention
Data retention is a critical aspect of data management, as it ensures that important information is kept for the appropriate amount of time. This can help organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements, as well as protect against potential litigation or investigation.
For example, in the healthcare industry, patient records must be retained for a specific period of time to comply with federal regulations. Similarly, financial institutions are required to retain certain financial records for a set period of time to comply with industry regulations.
Types of Data Retention Policies
There are several types of data retention policies, each with their own unique requirements and considerations:
- Regulatory Retention: This type of retention is required by law or industry regulations. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires organizations to retain certain personal data for specific periods of time.
- Business Retention: This type of retention is based on an organization’s specific business needs. For example, a company may choose to retain customer data for a certain period of time to improve their marketing efforts.
- Legal Retention: This type of retention is required for potential litigation or investigation purposes. For example, organizations may be required to retain data related to a legal case for a set period of time.
Key Components of a Data Retention Policy
A comprehensive data retention policy should include the following key components:
- Identification of data types and sources: This component involves identifying the types of data that will be retained, as well as the sources of that data. For example, an organization may choose to retain customer data from their website, social media, and email marketing campaigns.
- Retention periods and criteria for the disposal of data: This component involves determining how long data will be retained, as well as the criteria for disposing of that data once it is no longer needed. For example, an organization may choose to retain customer data for three years, after which it will be securely disposed of.
- Security and privacy considerations: This component involves ensuring that data is stored securely and that privacy considerations are taken into account. For example, an organization may choose to encrypt sensitive data and limit access to that data to authorized personnel only.
- Technology and storage solutions: This component involves determining the technology and storage solutions that will be used to retain data. For example, an organization may choose to use cloud storage or an on-premises server.
- Processes for monitoring and auditing compliance: This component involves establishing processes for monitoring and auditing compliance with the data retention policy. For example, an organization may choose to conduct regular audits to ensure that data is being retained and disposed of in accordance with the policy.
In summary, data retention is a critical aspect of data management that involves retaining data for a specific period of time based on business, legal, or regulatory requirements. A comprehensive data retention policy should include the identification of data types and sources, retention periods and criteria for disposal, security and privacy considerations, technology and storage solutions, and processes for monitoring and auditing compliance.
Data Retention Policies and Procedures
Putting in place retention policies and procedures can enable organisations to only retain data necessary for the purposes for which it is collected. Retention policies state what type of information is held by the organisation, what it is used for, and how long it should be retained. These policies establish standard retention periods for different categories of data the organisation holds and is extremely beneficial in maintaining GDPR compliance. In deciding on retention periods, organisations should consider any legal obligations imposed on them for retention, limitation periods for claims, organisational needs, and the quality of the data held. Any decision on retention periods should be proportionate. This means retention periods should appropriately balance the organisation’s needs against the impact of retention on individuals concerned.
Retention procedures ensure that data is destroyed appropriately and securely per the retention policies. This could be done in different ways depending on the organisation. A good example would be introducing an automated system which flags records for review or deletion after a set time limit. Retention policies could also include procedures for data sharing between two organisations including what happens when the data is no longer needed. This could contain procedures for the recipient returning all shared data to the supplier without keeping any copies. It could also include all organisations involved deleting any copies of any data shared between them where it is no longer needed.
Why is data retention important?
Data retention is the practice of keeping and storing data for a specific period of time. It has become increasingly important for organizations today, given the rising volume of data being generated and the need to comply with legal and regulatory requirements. There are several reasons why data retention is important for organizations today, including:
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Organizations are often required by law to retain certain data for specific periods of time. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in legal, financial, and reputational consequences. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires organizations to retain personal data only for as long as it is necessary for the purpose for which it was collected. Failure to comply with this regulation can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of the organization’s global annual revenue, whichever is higher.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Having a robust data retention policy can help organizations recover from disasters or system failures. By retaining critical data, organizations can restore their systems to a previous state and minimize the impact of the disaster or failure. It can also enable business continuity by ensuring that critical data is available when needed. For example, if an organization experiences a system failure, it can use the retained data to restore its systems to a previous state and resume its operations.
Download this blogpost!
Knowledge Management and Historical Analysis
Retaining data can enable organizations to analyze trends, gain insights, and make informed decisions. By analyzing historical data, organizations can identify patterns and trends that can help them make better decisions in the future. It can also support historical analysis and research. For example, historical sales data can be used to identify seasonal trends and plan marketing campaigns accordingly.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Data retention policies can help organizations provide adequate security and privacy protection to sensitive data while reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access. By retaining data for a specific period of time, organizations can monitor and track access to sensitive data and take appropriate action if necessary. It can also help organizations comply with data protection regulations by ensuring that personal data is only retained for as long as it is necessary.
In conclusion, data retention is crucial for organizations today. It can help organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements, enable business continuity and disaster recovery, support knowledge management and historical analysis, and provide adequate security and privacy protection to sensitive data. Organizations should develop a robust data retention policy that takes into account these factors and ensures that data is retained for the appropriate period of time.
Implementing a Data Retention Policy
Implementing an effective data retention policy requires careful planning and execution. It is essential to have a well-thought-out plan that meets the organization’s business, legal, and regulatory requirements. The following steps can help organizations establish and maintain a successful data retention policy:
Assessing Your Organization’s Data Retention Needs
Before implementing a data retention policy, organizations must first determine what data they need to retain, for how long, and for what purposes. This includes identifying data sources, types, and formats. Conducting a thorough assessment of the organization’s data retention needs can help ensure that the policy is effective and meets the organization’s requirements.
During the assessment, it is essential to consider the type of data that the organization collects, processes, and stores. This can include customer data, financial records, employee records, and other sensitive information. It’s also important to consider the purpose of the data and how long it needs to be retained. For example, some data may need to be retained for legal or regulatory reasons, while other data may only need to be retained for a short period.
Establishing Retention Periods and Storage Methods
Retention periods should be defined based on business, legal, and regulatory requirements. It’s important to organize data by type and importance to determine the best storage methods, such as cloud-based storage or physical storage devices. Organizations should also consider the security of the storage methods and ensure that they are compliant with relevant regulations.
It’s important to regularly review retention periods and storage methods to ensure they are still appropriate and effective. Changes in business or regulatory requirements may require adjustments to the data retention policy.
Communicating and Training Employees on Data Retention Policies
It’s essential to communicate policies and procedures to employees and ensure they are trained on how to comply with them. This can include establishing user access controls and authentication policies. Employees should be informed of the organization’s data retention policy, including what data needs to be retained, how long it needs to be retained, and how it should be stored.
Training can also help employees understand the importance of data retention and how it can benefit the organization. This can include educating employees on the risks associated with data loss and the importance of protecting sensitive information.
Monitoring and Auditing Data Retention Practices
Regular monitoring and auditing can help identify any gaps or non-compliance issues in data retention practices. This can include testing data recovery procedures and assessing log and audit trails. It’s important to regularly review data retention practices to ensure they are still effective and compliant with relevant regulations.
Monitoring and auditing can also help identify any potential security risks or breaches. This can help organizations take proactive measures to protect sensitive data and prevent data loss.
Implementing a data retention policy is an essential part of any organization’s data management strategy. By following these steps, organizations can establish and maintain an effective data retention policy that meets their business, legal, and regulatory requirements.
Challenges and Best Practices in Data Retention
Despite the numerous benefits of data retention policies, there are also several challenges organizations may face. The following best practices can help mitigate these challenges:
Balancing Data Retention and Storage Costs
Data retention policies can lead to increased storage costs. Organizations should consider implementing solutions that allow for automatic data deletion or archiving of less important data.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Ensuring security and privacy is critical in data retention policies. Strategies can include limiting access controls, establishing data classification policies, and implementing encryption for sensitive data.
Adapting to Changing Regulations and Industry Standards
Regulations and industry standards can change rapidly, and organizations must be prepared to adapt their data retention policies accordingly. Regularly reviewing and updating policies can help keep organizations compliant.
Leveraging Technology Solutions for Data Retention Management
Technology solutions, such as data management software, can help organizations automate and streamline data retention processes. This can help reduce costs and ensure compliance.
Enforcement
Given some of the other drastic breaches of GDPR which could be committed by organisations, some might think cracking down on retention periods would be at the bottom of the list. However, this is far from reality. In 2019, a German real estate company was fined €14.5 million for retaining data regarding tenants that was no longer required and had no legal basis for being retained. Organisations need to take a proactive approach to understand what data is held, why, and whether it should still be held. Data retention principles must be prioritised across all organisations, not just those who process data on a large scale. Organisations need to meaningfully engage in reviewing the data they hold and shake off the attitude of keeping data “just in case”.
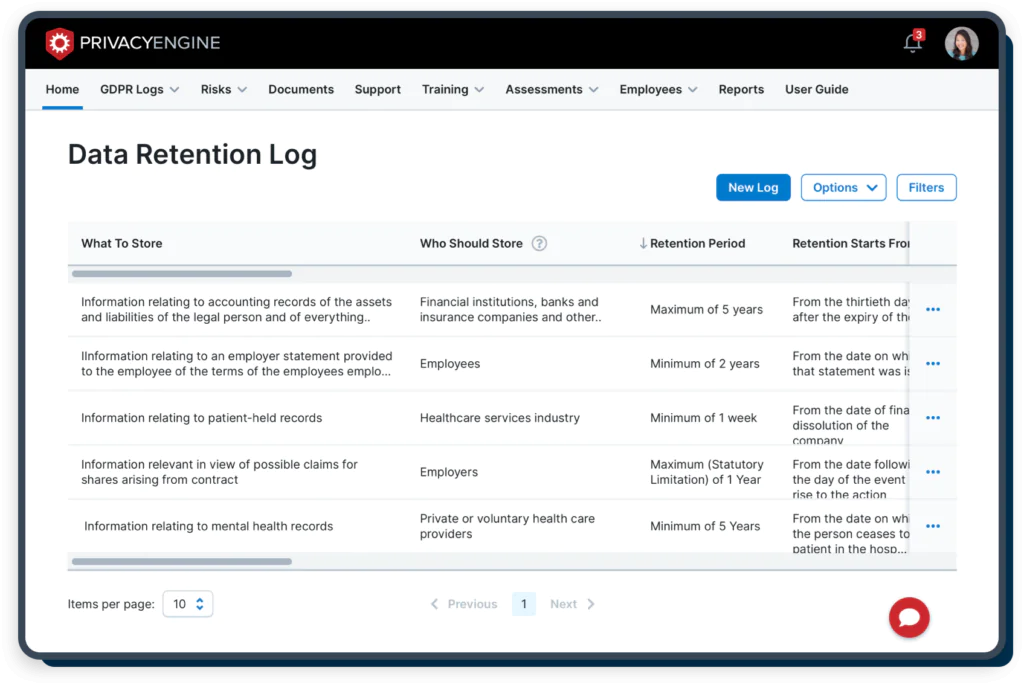
With PrivacyEngine, your organisation can get instant access to retention schedules for over 140 countries with over 100,000 periods defined. Not sure how long you can hold onto data for? PrivacyEngine instantly provides information on retention periods with one click of a button!
Learn how your organisation can comply with data retention requirements across multiple jurisdictions and critical business functions and also save time and money, by booking a meeting with a member of the PrivacyEngine team and discuss how our Data Retention Software is a match for you.
Data Retention Principles
The data retention principle refers to the set of policies and guidelines that govern the length of time organizations keep certain types of data. The principles of data retention vary depending on the industry, jurisdiction, and type of data involved. However, some common data retention principles include:
- Legal compliance: Organizations must retain data for the minimum amount of time required by law. For example, tax authorities may require financial records to be kept for several years.
- Business requirements: Certain data may need to be retained for business purposes such as auditing, financial reporting, or to support ongoing operations.
- Data minimization: Organizations should only retain data that is necessary for specific purposes and should dispose of it when it is no longer required.
- Data security: Retained data should be protected from unauthorized access, modification, or loss.
- Transparency: Organizations should have clear policies and procedures for data retention, and communicate these policies to relevant stakeholders.
It’s important to note that the principles of data retention are subject to change as new laws and regulations are enacted and technology evolves. Organizations must continuously review and update their data retention policies to ensure they are in compliance with the latest standards.
Conclusion
Data retention policies are crucial for organizations to effectively manage their data in today’s digital age. A comprehensive data retention policy can help organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements, support business continuity and disaster recovery, and provide secure and privacy-protected storage options. Implementing effective data retention policies requires careful planning, clear communication, and ongoing monitoring and auditing.
Find out more. Schedule your demo today!